Master Grease Trap Sizing and Installation: Ultimate Guide
Grease traps are essential for maintaining the efficiency of wastewater systems in both commercial and residential settings. Proper grease trap sizing and installation ensure that fats, oils, and grease (FOG) are effectively intercepted before they enter the sewage system, preventing blockages and environmental damage.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about sizing and installing grease traps.
Key Takeaway
Correctly sizing and installing a grease trap ensures efficient wastewater management and prevents blockages. Whether you’re running a restaurant or managing a household, understanding the intricacies of grease traps can save you from costly repairs and environmental fines.
Why Grease Trap Sizing and Installation Matter

Proper grease trap sizing and installation are critical for several reasons:
- Prevents Blockages: Accumulated FOG can clog pipes and cause sewage backups.
- Environmental Compliance: Many local regulations require businesses to have properly functioning grease traps.
- Cost-Efficiency: Avoids costly repairs and downtime due to plumbing issues.
Understanding Grease Trap Basics

What is a Grease Trap?
A grease trap, also known as a grease interceptor, is a plumbing device designed to capture FOG from wastewater before it enters the sewage system. It essentially traps grease from kitchen wastewater, preventing it from clogging pipes.
How Does a Grease Trap Work?
Grease traps work on the principle that FOG is less dense than water. When wastewater enters the trap, it slows down, allowing grease to float to the top and solids to settle at the bottom. The cleaner water exits the trap, leaving the grease and solids behind.
Key Factors in Sizing a Grease Trap

Flow Rate
The flow rate of the wastewater is a crucial factor in determining the size of a grease trap. It is measured in gallons per minute (GPM). Higher flow rates require larger grease traps to effectively capture FOG.
Kitchen Equipment
The type and number of kitchen appliances impact the amount of grease produced. Dishwashers, sinks, and cooking equipment all contribute to the FOG levels in wastewater.
Usage Frequency
The frequency of use also affects the grease trap size. High-usage kitchens, such as those in restaurants, need larger grease traps compared to smaller, less-frequented ones like in residential settings.
Calculating the Right Size for Your Grease Trap
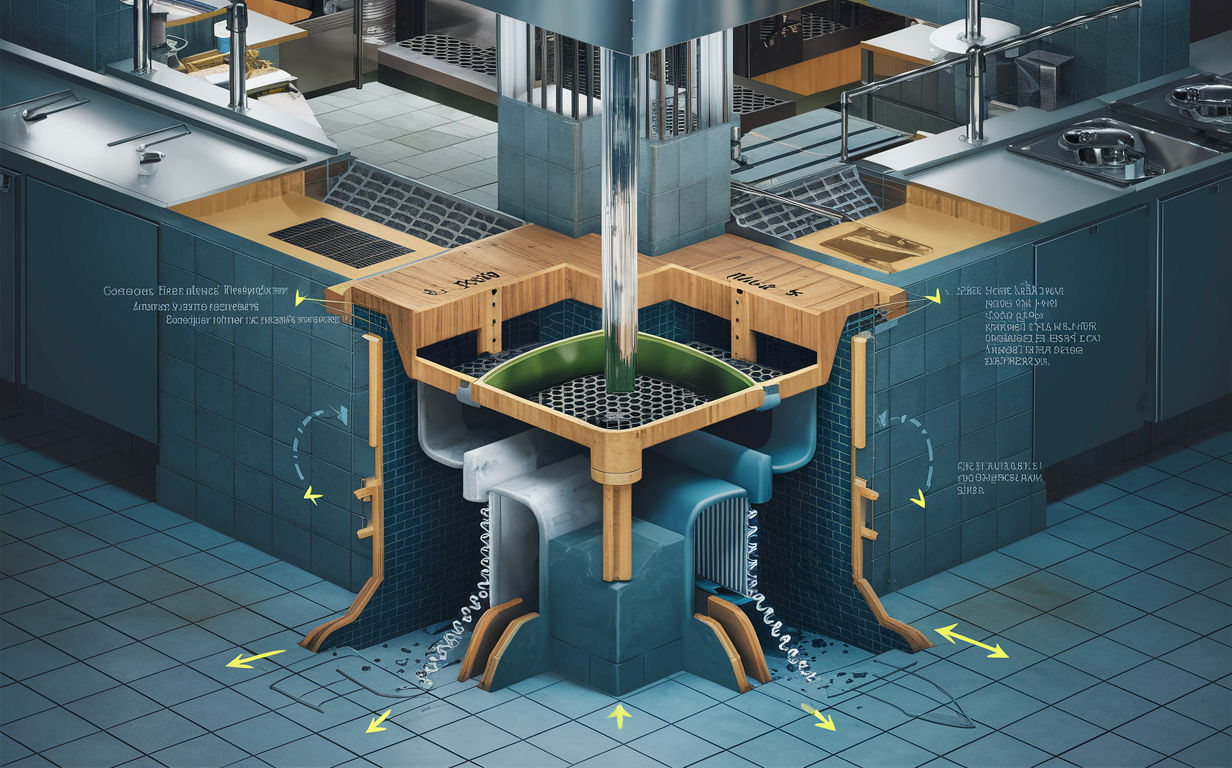
To calculate the proper size of a grease trap, follow these steps:
- Measure All Fixtures: Determine the volume of potential grease-producing fixtures.
- Calculate Flow Rate: Sum up the flow rates of all fixtures in gallons per minute (GPM).
- Apply Sizing Formula: Use the formula: Grease Trap Size (GPM) = Total Flow Rate (GPM) x Retention Time (minutes).
Grease Trap Installation Process

Selecting the Location
Choose a location close to the grease-producing fixtures but easily accessible for maintenance. Ensure it’s in compliance with local regulations.
Preparing the Site
Excavate the area if necessary and prepare the drainage system. Make sure the site is level and stable to support the grease trap.
Installing the Grease Trap
- Connect Inlet and Outlet Pipes: Securely connect the pipes to the grease trap, ensuring there are no leaks.
- Seal the Joints: Use appropriate sealants to prevent leakage.
- Test the System: Run water through the system to check for any issues.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting

Regular Cleaning
Regularly clean the grease trap to maintain its efficiency. The frequency depends on the usage and size of the trap.
Monitoring
Install grease trap monitors to keep track of FOG levels and ensure timely cleaning.
Facts About Grease Trap Sizing And Installations
- According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), grease traps are required in food service establishments to prevent fats, oils, and greases (FOG) from entering the sewer system and causing blockages [1].
- The size of a grease trap depends on the size of the kitchen and the amount of FOG produced. For instance, a small restaurant with a capacity of 50 seats may require a grease trap with a capacity of 500 gallons, while a large restaurant with a capacity of 500 seats may need a grease trap with a capacity of 2,000 gallons [2].
- The National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) sets the standard for grease trap design and installation. NSF-certified grease traps must meet specific performance requirements, including a minimum flow rate of 25 gallons per minute and a minimum grease removal capacity of 35% [3].
- Grease trap installations should be done by a professional plumber to ensure proper sizing and installation. Improper installation can lead to ineffective grease trap performance and potential health hazards [4].
- Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the grease trap is functioning properly. This includes regular cleaning, inspections, and repairs. The frequency of maintenance depends on the amount of FOG produced and the size of the grease trap [5].
Sources:
- EPA: Food Service Establishments and Grease Traps
- Restaurant Engine: Grease Trap Sizing Guide for Restaurants
- NSF: Grease Interceptors
- Plumbing Network: Plumbing Code Requirements for Grease Traps
- Restaurant.com: Grease Trap Maintenance
Common Issues
- Overflow: Caused by improper sizing or delayed maintenance.
- Foul Odors: Indicate a need for cleaning or possible leaks.
Comparison Table for Grease Trap Sizes
| Fixture Type | Flow Rate (GPM) | Average Usage (hours/day) | Recommended Trap Size (GPM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Compartment Sink | 15 | 8 | 100 |
| Double Compartment Sink | 30 | 10 | 200 |
| Dishwasher | 20 | 6 | 120 |
| Combination of All | 65 | 24 | 420 |
Additional Tips for Effective Grease Trap Management
- Employee Training: Educate staff on the importance of not pouring grease down the drain.
- Use Drain Screens: Install screens to catch food particles before they enter the grease trap.
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the grease trap for any wear and tear.
Common Misconceptions About Grease Traps
“Grease Traps Don’t Need Maintenance”
Regular maintenance is crucial for the efficient functioning of a grease trap. Neglecting it can lead to costly repairs and environmental fines.
“Any Size Will Do”
Using an incorrectly sized grease trap can lead to frequent overflows and blockages. Always calculate the proper size based on your specific needs.
Industry Standards and Regulations
Adhering to local regulations and industry standards is essential for grease trap installation. Ensure you are compliant with:
- Local Health Department Regulations
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Guidelines
- Plumbing Codes
Grease Trap Sizing Based on Flow Rate T
| Flow Rate (GPM) | Retention Time (minutes) | Grease Trap Size (GPM) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 200 |
| 20 | 20 | 400 |
| 30 | 20 | 600 |
| 40 | 20 | 800 |
| 50 | 20 | 1000 |
Key Takeaways for Efficient Grease Trap Management
- Correct Sizing: Ensure your grease trap is properly sized based on flow rate and usage.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean and inspect your grease trap regularly.
- Employee Training: Educate staff on proper grease disposal practices.
- Compliance: Adhere to local regulations and industry standards.
Conclusion
Proper grease trap sizing and installation are crucial for efficient wastewater management. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can ensure your system runs smoothly, preventing blockages and complying with environmental regulations.
Whether you’re a business owner or a homeowner, investing in a well-sized and well-maintained grease trap can save you from costly repairs and downtime.







 Texway Wastewater Services is a septic, wastewater, and excavation company based out of Burleson, Texas and serving the surrounding areas. We specialize in
Texway Wastewater Services is a septic, wastewater, and excavation company based out of Burleson, Texas and serving the surrounding areas. We specialize in